The cell membrane has immense medical importance since practically all drug molecules have their target in the membrane or must cross it if they have an intracellular binding site. In addition, the properties of membrane proteins are substantially influenced by the lipid composition of the cell membrane. These have medical implications for the following reasons:
- several diseases (e.g. lysosomal storage disorders, inherited or acquired dyslipidemias, malignant diseases) are accompanied by alterations in the lipid composition of the serum and the cell membrane, which impacts the functioning of membrane proteins (e.g. by mechanisms mentioned in point 2)
- the lipid composition of the cell membrane can be altered for therapeutical purposes, which can change the symptoms or course of several diseases.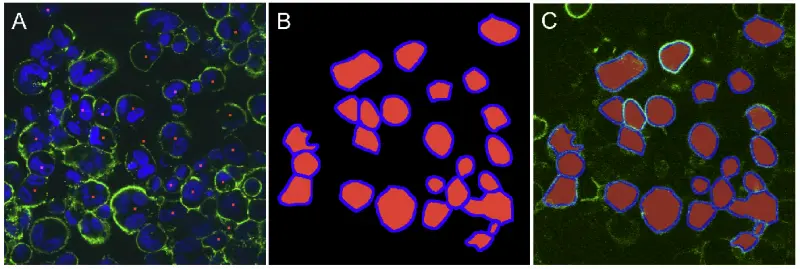
- several diseases (e.g. lysosomal storage disorders, inherited or acquired dyslipidemias, malignant diseases) are accompanied by alterations in the lipid composition of the serum and the cell membrane, which impacts the functioning of membrane proteins (e.g. by mechanisms mentioned in point 2)
- the lipid composition of the cell membrane can be altered for therapeutical purposes, which can change the symptoms or course of several diseases.
We have established that
- sphingolipid accumulation, typical of Gaucher’s disease, also involving the cell membrane, induces several changes in the properties of the cell membrane, e.g. reduced fluidity, inhibited STAT signaling and endocytosis of non-raft proteins. Measurement of endocytosis was carried out using confocal microscopy as demonstrated by the figure below.

A – Labeling of the cell membrane with anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody (green) and DAPI (blue), which stains the nucleus. Red dots corresponds to nuclei.
B – The cell membrane (blue) and the intracellular space (red) identified using the membrane and nuclear stains.
C – Overlay of the fluorescence image on the membrane and intracellular masks.
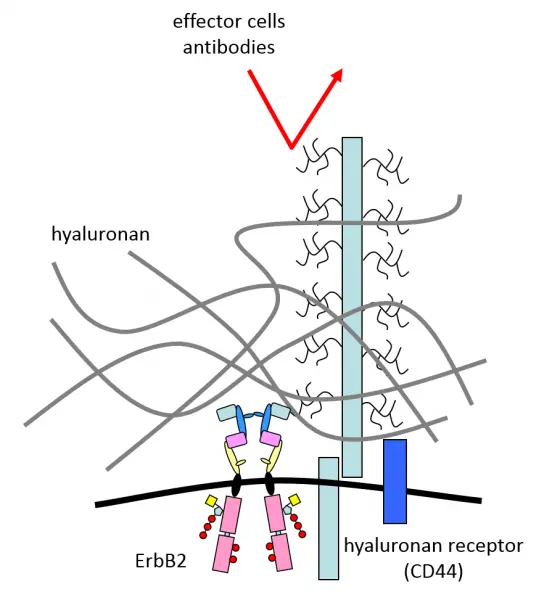
- binding of trastuzumab (Herceptin), used in the therapy of ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancers, to the cell membrane is inhibited by overexpression of the MUC-4 mucin and overproduction of hyaluronan.

In our current research efforts we would like to shed light on
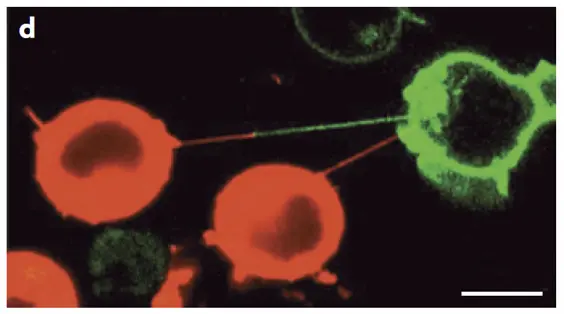
- how alterations in the lipid composition of the cell membrane change the generation of membrane nanotubes (see image below) and extracellular vesicles. Both nanotubes and extracellular vesicles are important means of intercellular communication. Changes in the generation are involved in the pathogenesis of immunological and malignant diseases.

Last update:
2023. 06. 21. 11:46