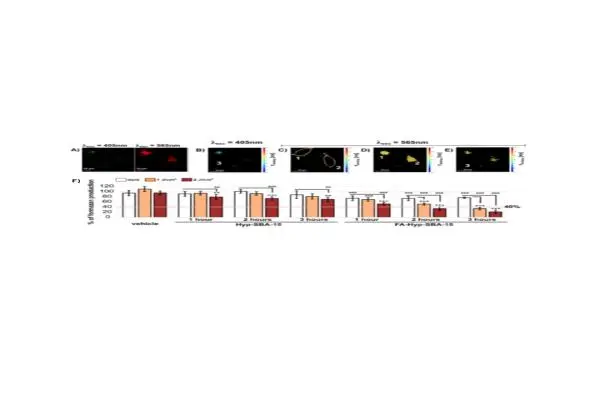
 In this collaborative work between Veronika Huntošová from the University of Kosice and Anass Benziane and György Vámosi from the Protein Dynamics and Interactions Research Group, cancer-targeting nanoparticles were tested using. Transport systems are developed to improve the solubility of the transported drug, increase its stability, enhance its pharmacological activity, and target cancer while minimising side effects. In this work, nanoporous silica particles that can be functionalized and loaded with a large number of hydrophobic molecules were used. The designed system was modified with folic acid to target the folic acid receptors of cancer cells. This modification enabled a higher uptake of the drug by the cells. Hypericin was selected as a hydrophobic molecule/drug with photodynamic properties suitable for diagnosis and therapy. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry were used to detect the targeting and distribution of hypericin in the cancer cells. Furthermore, they have shown that the combination of folic acid and singlet oxygen-forming hypericin have a synergistic effect in improving the efficacy of photodynamic therapy. The functionalisation of the particles proposed in this work holds great potential for the delivery of hydrophobic drugs to other types of cancer cells with increased expression of the folic acid receptor to which the particles can be attached.
In this collaborative work between Veronika Huntošová from the University of Kosice and Anass Benziane and György Vámosi from the Protein Dynamics and Interactions Research Group, cancer-targeting nanoparticles were tested using. Transport systems are developed to improve the solubility of the transported drug, increase its stability, enhance its pharmacological activity, and target cancer while minimising side effects. In this work, nanoporous silica particles that can be functionalized and loaded with a large number of hydrophobic molecules were used. The designed system was modified with folic acid to target the folic acid receptors of cancer cells. This modification enabled a higher uptake of the drug by the cells. Hypericin was selected as a hydrophobic molecule/drug with photodynamic properties suitable for diagnosis and therapy. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry were used to detect the targeting and distribution of hypericin in the cancer cells. Furthermore, they have shown that the combination of folic acid and singlet oxygen-forming hypericin have a synergistic effect in improving the efficacy of photodynamic therapy. The functionalisation of the particles proposed in this work holds great potential for the delivery of hydrophobic drugs to other types of cancer cells with increased expression of the folic acid receptor to which the particles can be attached.
Synergistic effect of folic acid and hypericin administration to improve the efficacy of photodynamic therapy via folate receptors
Synergistic effect of folic acid and hypericin administration to improve the efficacy of photodynamic therapy via folate receptors
Last update:
2024. 11. 13. 09:02