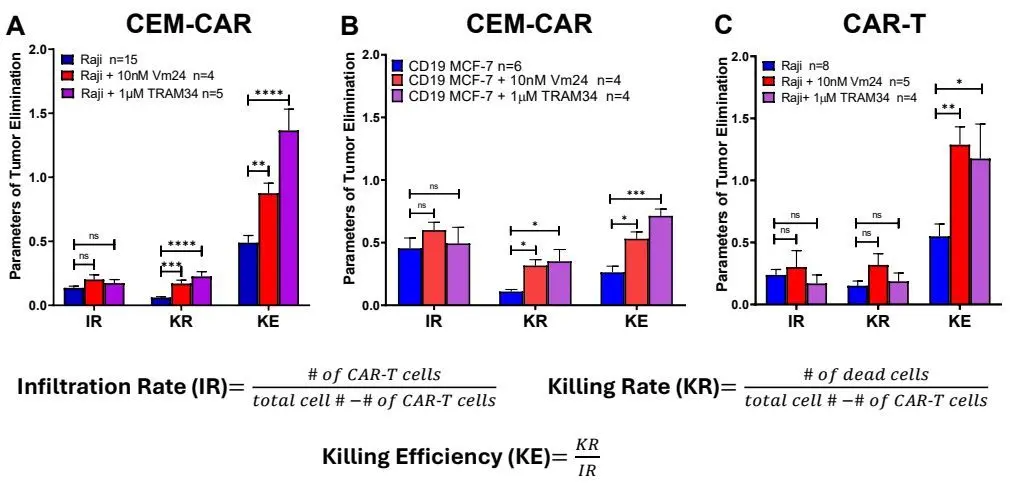
 T cells with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR-T cells), created by genetically modifying T cells, are able to recognize a specific antigen on the tumor surface and then destroy the tumor. T lymphocyte ion channels, such as Kv1.3, KCa3.1 and CRAC, influence T cell activation, proliferation and some effector functions, such as cytokine release, migration and even target cell killing, by regulating Ca2+ signaling. Two CAR cell lines (from CEM T-cell line and primary T-cells) have been generated that recognize the CD19 antigen on the surface of Raji B cells and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Firstly, electrophysiological measurements showed that the functional expression of KCa3.1 and Kv.3 in CEM cells was like that of T cells, demonstrating their suitability for modeling primary T cells. The tumor cell killing efficacy of CAR-T and CEM-CAR cells was then examined in monolayer culture and 3D spheroid tumor models. They successfully demonstrated that CEM-CAR and CAR-T cells specifically eliminate tumor cells independently of tumor models. Furthermore, the use of Kv1.3 (Vm24) and KCa3.1 (TRAM34) inhibitors significantly improved tumor killing efficiency of both CEM-CAR and CAR-T cells in tumor spheroids, but infiltration was not affected using antagonists. It was concluded that modification of Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 ion channels might contribute to more effective immunotherapy of solid tumors.
T cells with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR-T cells), created by genetically modifying T cells, are able to recognize a specific antigen on the tumor surface and then destroy the tumor. T lymphocyte ion channels, such as Kv1.3, KCa3.1 and CRAC, influence T cell activation, proliferation and some effector functions, such as cytokine release, migration and even target cell killing, by regulating Ca2+ signaling. Two CAR cell lines (from CEM T-cell line and primary T-cells) have been generated that recognize the CD19 antigen on the surface of Raji B cells and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Firstly, electrophysiological measurements showed that the functional expression of KCa3.1 and Kv.3 in CEM cells was like that of T cells, demonstrating their suitability for modeling primary T cells. The tumor cell killing efficacy of CAR-T and CEM-CAR cells was then examined in monolayer culture and 3D spheroid tumor models. They successfully demonstrated that CEM-CAR and CAR-T cells specifically eliminate tumor cells independently of tumor models. Furthermore, the use of Kv1.3 (Vm24) and KCa3.1 (TRAM34) inhibitors significantly improved tumor killing efficiency of both CEM-CAR and CAR-T cells in tumor spheroids, but infiltration was not affected using antagonists. It was concluded that modification of Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 ion channels might contribute to more effective immunotherapy of solid tumors.
The results of the study were published in The Journal of Immunology.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jimmun/vkaf084
Role of CAR-T cell K+ channels in tumor infiltration and elimination
Vivien Jusztus, Árpád Szöőr and Péter Hajdu investigated the role of CAR-T cell potassium channels in tumor infiltration and elimination.
Last update:
2025. 05. 21. 10:07