 Kipchumba Biwott, Zsolt Bacso, along with their colleagues and collaborators, investigated how ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of hematologic cancers and inflammatory diseases, modulated immune cell function, particularly in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Their research focused on P-glycoprotein (Pgp/ABCB1), a drug transporter protein associated with multidrug resistance and immune regulation.
Kipchumba Biwott, Zsolt Bacso, along with their colleagues and collaborators, investigated how ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of hematologic cancers and inflammatory diseases, modulated immune cell function, particularly in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Their research focused on P-glycoprotein (Pgp/ABCB1), a drug transporter protein associated with multidrug resistance and immune regulation.
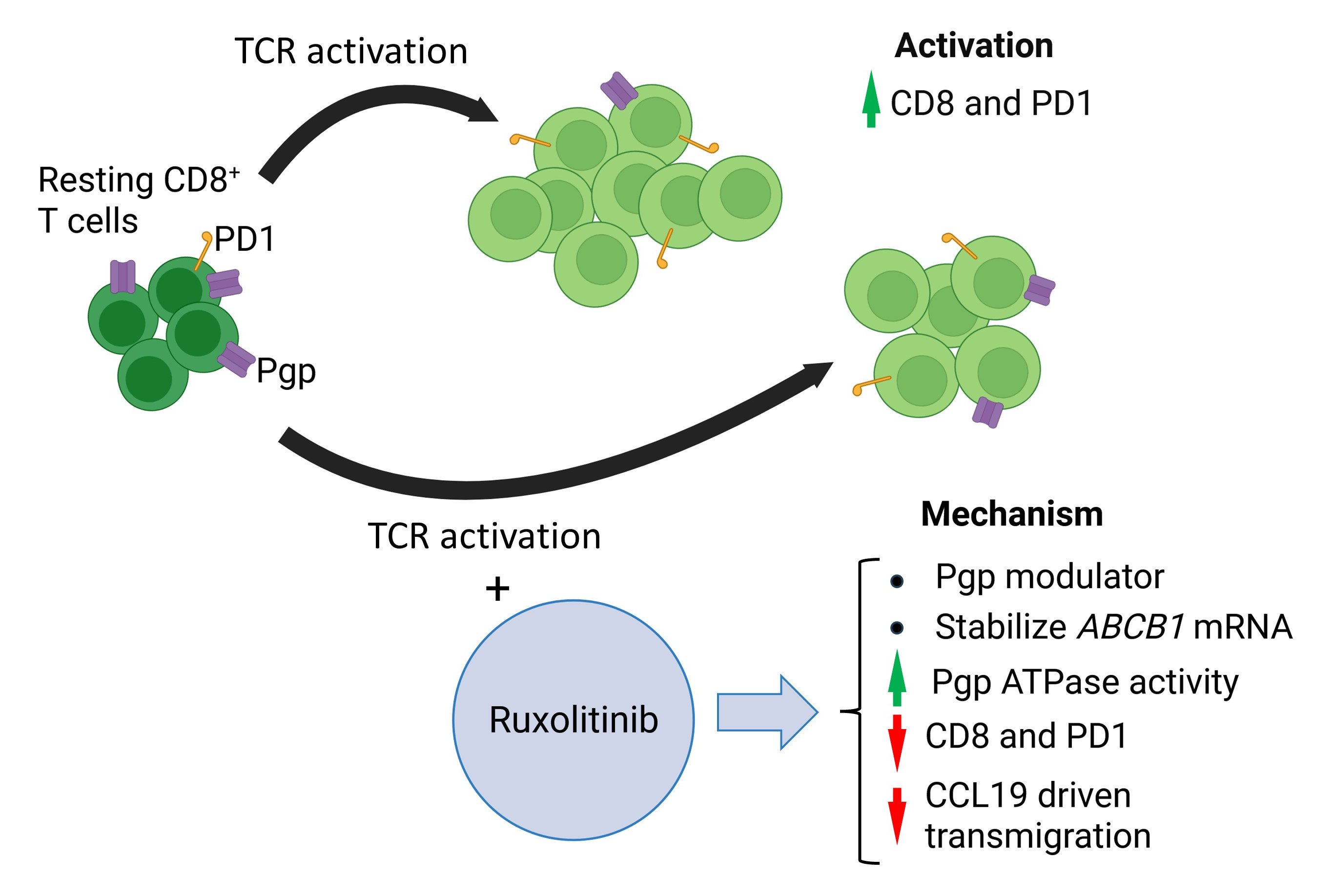
They demonstrated that human CD8⁺ T cells expressed Pgp in a dynamic, activation-dependent manner at both the mRNA and protein levels. Using functional assays, they found that ruxolitinib increased calcein retention and enhanced basal ATPase activity at higher concentrations (10–100 μM), a similar effect to that of verapamil, a known Pgp modulator. At these supratherapeutic levels, ruxolitinib appeared to interfere directly with Pgp’s transport function.
More importantly, at clinically relevant plasma concentrations (1–3 μM), ruxolitinib stabilized Pgp mRNA during early T cell receptor (TCR) activation and suppressed TCR-induced upregulation of surface markers, including Pgp, CD8, and PD-1. Additionally, ruxolitinib reduced the ability of CTLs to migrate across endothelial barriers in response to CCL19, a key chemokine involved in the homing of lymphoid tissue.
These findings demonstrated that ruxolitinib modulated Pgp expression and function in a concentration-dependent manner, significantly affecting T cell activation and migration. The study highlights the importance of evaluating JAK inhibitor-driven immune modulation in therapeutic approaches, such as vaccination, transplantation, and T-cell-based treatments.
DOI https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136123
Link https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/13/6123
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26(13), 6123
Ruxolitinib Modulates P-Glycoprotein Function, Delays T Cell Activation, and Impairs CCL19 Chemokine-Directed Migration in Human Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
Ruxolitinib Modulates P-Glycoprotein Function, Delays T Cell Activation, and Impairs CCL19 Chemokine-Directed Migration in Human Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
Last update:
2025. 08. 22. 13:34